Outbreak of Lung Disease Associated with E-Cigarette Use, or Vaping
Posted September 12, 2019 at 6:15pm ET
CDC, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), state and local health departments, and other clinical and public health partners are investigating a multistate outbreak of lung disease associated with e-cigarette product (devices, liquids, refill pods, and/or cartridges) use.
Key Facts about E-Cigarette Use, or Vaping
· Electronic cigarettes – or e-cigarettes — are also called vapes, e-hookahs, vape pens, and electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS).
· Using an e-cigarette product is commonly called vaping.
· E-cigarettes work by heating a liquid to produce an aerosol that users inhale into their lungs.
· The liquid can contain: nicotine, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabinoid (CBD) oils, and other substances and additives.
On This Page
· Key Facts about E-Cigarette Use, or Vaping
For the Public: What You Need to Know
For State and Local Health Departments
· There are 380* cases of lung illness reported from 36 states and 1 U.S. territory. Six deaths have been reported from 6 states.
· All reported cases have a history of e-cigarette product use or vaping.
· Most patients have reported a history of using e-cigarette products containing THC. Many patients have reported using THC and nicotine. Some have reported the use of e-cigarette products containing only nicotine.
· We do not yet know the specific cause of these illnesses. The investigation has not identified any specific e-cigarette or vaping product (devices, liquids, refill pods, and/or cartridges) or substance that is linked to all cases.
· CDC has released interim recommendations for healthcare providers, health departments, and the public.
· Until we know more, if you are concerned about these specific health risks, CDC recommends that you consider refraining from using e-cigarette or vaping products.
· If you are an adult who used e-cigarettes containing nicotine to quit cigarette smoking, do not return to smoking cigarettes.
· If you have recently used an e-cigarette or vaping product and you have symptoms like those reported in this outbreak see a healthcare provider.
· Regardless of the ongoing investigation:
o Anyone who uses an e-cigarette or vaping product should not buy these products (e.g., e-cigarette or vaping products with THC, other cannabinoids) off the street, and should not modify or add any substances to these products that are not intended by the manufacturer.
o Youth and young adults should not use e-cigarette products.
o Women who are pregnant should not use e-cigarette products.
o Adults who do not currently use tobacco products should not start using e-cigarette products.
Latest Outbreak Information on Lung Disease Associated with Electronic Cigarettes
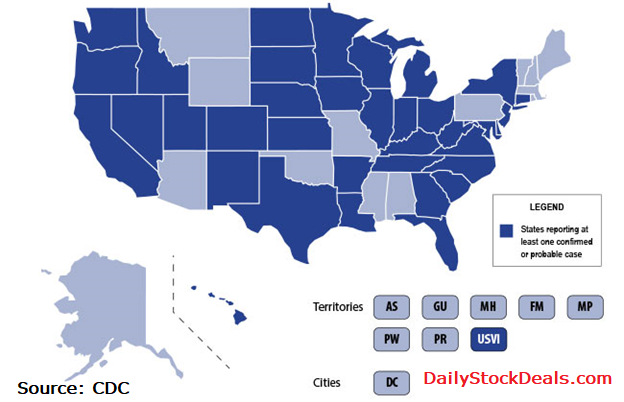
· As of September 11, 2019 at 5pm, 380* cases of lung illness associated with the use of e-cigarette products have been reported to CDC from the following states and 1 U.S. territory: AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, IA, ID, IL, IN, KS, KY, LA, MD, MI, MN, NC, ND, NE, NJ, NM, NV, NY, OH, OR, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VA, WA, WI, WV, and USVI. These numbers may change frequently.
· Six deaths have been confirmed in California, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Minnesota, and Oregon.
· CDC worked with states to create a case definition to classify confirmed and probable cases in a consistent way. State investigators determine if cases are confirmed or probable after examining the medical records of suspected cases and consulting with the clinical care team to exclude other possible causes of illness. Unlike nationally reportable conditions, these cases are requiring clinicians and public health professionals to interview patients to determine product use and individual behaviors.
· CDC will report numbers of confirmed and probable cases once states have finalized their classification of cases.
· States are in the process of classifying cases. We expect that states and clinicians may look back for older cases based on CDC’s case definition.
· All patients have a reported history of e-cigarette product use, and no consistent evidence of an infectious cause has been discovered. Therefore, the suspected cause is a chemical exposure.
· Most patients have reported a history of using e-cigarette products containing THC. Many patients have reported using THC and nicotine. Some have reported the use of e-cigarette products containing only nicotine.
· No consistent e-cigarette or vaping product, substance, or additive has been identified in all cases, nor has any one product or substance been conclusively linked to lung disease in patients.
· Initial published reports from the investigation point to clinical similarities among cases. Patients reported a history of e-cigarette use and had similar symptoms and clinical findings. These align with the CDC health advisory released August 30, 2019.
· These investigations are ongoing. CDC will provide updates when more information is available.
*The previous case count was higher because it reported possible cases that were under investigation by states. The current number includes only confirmed and probable cases reported by states to CDC after classification.




